In order to thoroughly assess a variant’s pathogenicity, it is important to take into account the variant’s effect on splicing. While the interpretation of variants that disrupt the pairs of bases at the beginning of a splice site is fairly straightforward, variants resulting in the introduction of a novel splice site are more difficult to interpret. In this blog post,… Read more »
While VarSeq has always had excellent support for variant interpretation and analysis, we continue to find new edge cases in the clinical literature that improve our interpretation capabilities. In this blog, we will be covering some of the new improvements in VarSeq to support the interpretation of non-coding and splice site variants. Transcript Annotation Improvements Let’s start by covering some… Read more »
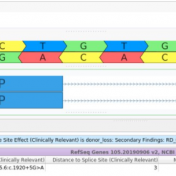
Our latest VarSeq release is one of the largest we’ve ever had, boasting an extensive list of new features and improvements. As part of this release, we have dramatically expanded our support for splice site analysis. This includes improvements to our novel splice site algorithm and support for splice site effect prediction along with several other small improvements. Novel Splice… Read more »
Revisiting the Five Splice Site Algorithms used in Clinical Genetics Interpretation of variants in accordance with the ACMG guidelines requires that variants near canonical splice boundaries be evaluated for their potential to disrupt gene splicing [1]. The five most common tools for splice site detection are NNSplice, MaxEntScan, GeneSplicer, HumanSplicingFinder, and SpliceSiteFinder-like. Because these algorithms have been made easily accessible… Read more »