An under-utilized use of VarSeq is the ability of mining raw variant data in GenomeBrowse for relevant literature. By bringing in various public and private annotation sources, GenomeBrowse allows the user to interface with raw variant data in a compressed and manageable view. This blog will show you how to leverage these sources to power up your search for variant… Read more »
When doing next-generation sequencing (NGS) analysis in VarSeq, the fundamental goal is to develop efficient ways to filter through your NGS data. If you are just getting started with Varseq, a pre-designed project template can really come in handy for variant filtering! This blog series will cover a number of template design recommendations for variant filtering on data types ranging… Read more »
Although best known for its auto-generation of custom reports, VarSeq comes with a slew of options for exporting your data. In this blog, we will review some of the lesser-known methods for exporting your data into usable formats. These four export options can all be found under the Export tab at the upper left corner of your VarSeq interface (Figure… Read more »
Thanks to all those who attended the recent webcast by Dr. Rana Smalling, “Integrating Custom Gene Panels for Variant Annotations”. If you were unable to attend or would like to recap, here is a link to watch the broadcast. We covered a lot of content regarding virtual gene panels, and there were several questions submitted during our Q&A session that… Read more »
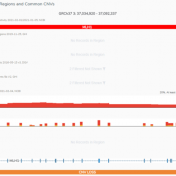
Global population frequency catalogs like 1kG Phase 3, gnomAD, DGV, and others are excellent resources for identifying rare variants in your copy number variant (CNV) analysis. However, they are not exhaustive, and the reality is a lot of variants that are missing from global population frequency catalogs are still common variants. At the same time, CNVs that are identified by… Read more »
If you stay current on the developments of Golden Helix features, you are aware of the substantial evolution of our copy number detection and evaluation capabilities in VarSeq. The process of CNV detection and evaluation is typically handled through the VarSeq graphic user interface. However, in some cases, users benefit from running this process via the command-line interface. Fortunately, Golden… Read more »
As a newer member of the Golden Helix FAS Team I, like many of our customers, went through a phase of learning the ins, outs, and shortcuts of clicking around the program. In an effort to expedite new users coming up to speed, or to teach some tricks to experienced users, I’ve compiled a list of the top things I… Read more »
The VarSeq CNV calling algorithm, VS-CNV, is a powerful tool for calling CNVs from the NGS coverage data stored in your BAM files. However, before this algorithm can be deployed in a clinical setting, it must be tuned and validated using data that is representative of your lab’s NGS workflow. In the past, this validation process could be difficult, as… Read more »
Clinical diagnostic efforts in next-generation sequencing are commonly defined at a gene panel level. The validation process of adding new genes to any diagnostic panel is ongoing, but labs typically construct and validate their clinical workflows for the current status of verified genes. This is not limited to primary finding results but can also include any incidental findings among the… Read more »
Clinical labs often maintain gene panels, which are lists of genes with evidence of disease association. These panels are used to prioritize variants and limit interpretations to a predefined set of test-specific genes. In general, gene panels should be stored independently of any specific project or interpretation, as it is common for an individual gene panel to be generally applicable… Read more »
Thanks for checking out this blog on how to to get more out of your VarSeq projects! The best way to show off one of my favorite new features that have been incorporated into the latest VarSeq 2.2.3 release is with a scenario: You work in a lab that processes and analyzes multiple whole exome samples for copy number variations,… Read more »
Thank you to those who attended the recent webcast, “High Precision Exome CNV Detection with VS-CNV”. For those who could not attend but wish to watch, here is a link to the recording. This webcast delved into the complex world of CNV calling for whole-exome samples, which presents unique challenges that require specific considerations and strategies. Over the past several months,… Read more »
In many cases, VarSeq users design their next-gen sequencing workflows for a clinical application. One of the major values of using VarSeq is the standardization of sample analysis via project templates for filtering down to rare variants and isolate any clinically relevant variant. However, VarSeq also doubles as a robust research application as well. There are specific algorithms that can… Read more »
While VarSeq has always had excellent support for variant interpretation and analysis, we continue to find new edge cases in the clinical literature that improve our interpretation capabilities. In this blog, we will be covering some of the new improvements in VarSeq to support the interpretation of non-coding and splice site variants. Transcript Annotation Improvements Let’s start by covering some… Read more »
Orphanet is a public database available in VarSeq that aims to improve the current understanding and treatment options for patients affected by rare diseases. This resource was established in France in 1997 and has gradually grown to cover a consortium of over 40 countries in Europe. The primary goal of this database is to provide a universal nomenclature to classify… Read more »
Clinical testing labs produce reports as the end product of the NGS variant detection and interpretation workflow. Necessarily, the content, detail, and presentation of the report needs to be specialized to each clinical lab, and potentially each offered test. Our last blog post introduced the new Word-based report templates in VSClinical. In this blog post, we will introduce and explore… Read more »
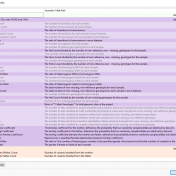
The collaboration between the Clinical Genome Resource (ClinGen) consortium and the American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) recently developed published guidelines for the interpretation of CNVs called on next-generation sequencing data. These new guidelines are the first to provide a robust set of rules for the interpretation of small intragenic deletions and duplications and are now automated in VSClinical. … Read more »
In many cases, VarSeq users typically run single trio projects or perhaps an extended family project. Not only are all the inheritance model algorithms available in the VarSeq software to capture de novo, dominant, or recessively inherited variants but there are a number of quality control fields to help ensure the pedigree was set up properly. The last thing any… Read more »
The recent release of VarSeq 2.2.2 brings our Word report template system, previously featured in VSClinical AMP, to the VSClinical ACMG workflow. This blog post will describe how to use the Word template system using one of our shipped templates as well as how to start customizing your own templates. We will cover the three different report templates that ship… Read more »
Thank you for attending the webinar focused on implementing VarSeq and VSClinical for family-based workflows. If you would like to use the webinar as a reference or were not able to attend, you can access it using the following link to view ‘Family-Based Workflows in VarSeq and VSClinical. Here is a brief recap of what we discussed: This webinar demonstrated… Read more »