About Nathan Fortier
Nathan Fortier, Ph.D, Director of Research for Golden Helix, joined the development team in June of 2014. Nathan obtained his Bachelor’s degree in Software Engineering from Montana Tech University in May 2011, received a Master’s degree in Computer Science from Montana State University in May 2014, and received his Ph.D. in Computer Science from Montana State University in May 2015. Nathan works on data curation, script development, and product code. When not working, Nathan enjoys hiking and playing music.
Our latest VarSeq release is one of the largest we’ve ever had, boasting an extensive list of new features and improvements. As part of this release, we have dramatically expanded our support for splice site analysis. This includes improvements to our novel splice site algorithm and support for splice site effect prediction along with several other small improvements. Novel Splice… Read more »
We have had many customers come to us over the years with a simple problem: they have BAM files for whole exome or gene panel data and would like to call CNVs using VarSeq’s powerful CNV calling capabilities, but they don’t have a bed file defining the target regions for their samples. To address this problem, we have developed a… Read more »
Abstract Before assessing the clinical significance of a somatic mutation, one must determine if the mutation is likely to be a driver mutation (i.e. a mutation that provides a selective growth advantage, thereby promoting cancer development). To aid clinicians in this process, VSClinical provides an oncogenicity scoring system, which uses a variety of metrics to classify a given somatic mutation… Read more »
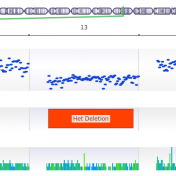
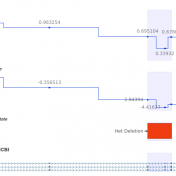
In trio workflows, one of the most important factors in scoring a variant is understanding how that variant is inherited from the parents. Likewise, when looking at extended families, the segregation, or presence of the variant among the affected versus unaffected individuals provides evidence for its pathogenicity for a given phenotype or disease. Given the nature of Copy Number Variants… Read more »
When interpreting a variant using the AMP/ASCO guidelines for somatic variant interpretation, clinicians must determine whether the variant can be considered a biomarker that affects clinical care by predicting sensitivity, resistance, or toxicity to a specific therapy. Such a determination requires the investigation of multiple evidence sources, including clinical trials, FDA approved therapies and peer-reviewed studies. Unfortunately, strong evidence linking… Read more »
Before examining the clinical evidence associated with a specific mutation, a clinician must establish that the variant is likely to be a driver mutation which generates functional changes that enhance tumor cell proliferation. Our recent blog series “Following the AMP Guidelines with VSClinical” briefly mentioned how the oncogenicity scoring system in VSClinical could be used to automate and assist the… Read more »
We are happy to announce that our latest version of SVS includes the ability to call CNVs on low read depth Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) data. Designed for calling large cytogenetic events, this algorithm can detect chromosomal aneuploidy events and other large events spanning one or more bands of a chromosome from genomes with average coverage as low as 0.05x…. Read more »
We love when our viewers send questions in during the webcast but unfortunately we can’t answer all of them during the time allotted! If you asked a question see below for answers, or if after viewing, you have any questions that weren’t asked, please feel free to send those over to support@goldenhelix.com. Does this work for FFPE derived DNA or ctDNA?… Read more »
In our previous webcast, we discussed the splice site algorithms for clinical genomics within VSClinical. We took it a step further in yesterday’s webcast and looked at the functional predictions and conservation scores. We had a great turnout for this event with lots of great questions from the attendees. I’d like to recap our Q&A for anyone else who might… Read more »
Functional Predictions and Conservation Scores in VSClinical Several algorithms have been developed to predict the impact of amino acid substitutions on protein function and quantify conservation of nucleotide positions. These methods provide vital supporting evidence to clinicians when interpreting variants in accordance with the ACMG guidelines. The two most popular functional prediction algorithms are SIFT and PolyPhen2, while the most… Read more »
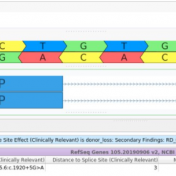
Revisiting the Five Splice Site Algorithms used in Clinical Genetics Interpretation of variants in accordance with the ACMG guidelines requires that variants near canonical splice boundaries be evaluated for their potential to disrupt gene splicing [1]. The five most common tools for splice site detection are NNSplice, MaxEntScan, GeneSplicer, HumanSplicingFinder, and SpliceSiteFinder-like. Because these algorithms have been made easily accessible… Read more »
Interpretation of variants in accordance with the ACMG guidelines requires that variants near canonical splice boundaries be evaluated for their potential to disrupt gene splicing [1]. The five most common tools for splice site detection are NNSplice, MaxEntScan, GeneSplicer, HumanSplicingFinder, and SpliceSiteFinder-like. Because these algorithms have been made easily accessible in the bioinformatics tool Alamut, they have been canonized for… Read more »
Low read depth? Great! We are excited to introduce our new CNV calling algorithm for low and ultra-low read depth Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) data. This algorithm is designed to call large cytogenetic events with high confidence from low read depth whole genome data, with as few as one million aligned reads or 0.02x coverage. The low sequencing cost of… Read more »
In our latest VarSeq release, we updated our PhoRank algorithm with the ability to specify OMIM phenotype terms not present in HPO, as well as a general update to the algorithm to improve the results. In this post, we review the fundamentals of how PhoRank determines the ranking of genes in your VarSeq projects based on your input phenotype terms… Read more »
When the new human reference genome was released over two years ago, it was hailed as a significant step forward for next generation sequencing. Compared to GRCh37, the new GRCH38 reference assembly fixed gaps, repaired incorrect sequences and offered access to sections of the genome that had been previously unaccounted for. Despite these improvements, adoption of the new assembly has… Read more »
Golden Helix is proud to announce the release of the Golden Helix GenomeBrowse Plugin for Ion Torrent server. The new plug-in enables adding selected BAM files from Torrent Server reports directly into GenomeBrowse. The BAM files remain on the torrent server and are streamed from the server on demand using your credentials. This feature allows GenomeBrowse users to visualize genomic… Read more »